
The Complete Guide to Non-Woven Geotextiles
Non-woven geotextiles are an important category of geosynthetics used across a wide range of infrastructure and construction applications. This guide provides a deep dive into what non-wovens are, their types, key properties, manufacturing processes, installation methods, advantages, applications, and more.

Introduction to Non-Woven Geotextiles
Geotextiles refer to permeable, polymeric textile materials used in contact with soil or rock in civil engineering applications. They can be woven or non-woven.
Non-woven geotextiles are made by bonding polymeric fibers together through processes like needle punching, heat bonding or resin bonding. The random arrangement of fibres produces a strong, porous and flexible material.
Geotextiles that are non-woven are better than those that are woven. They are better at filtering, draining, and cushioning, and are easier to install. In addition, they are more budget-friendly. These characteristics make non-wovens ideal for many functions like filtration, drainage, separation, and reinforcement.
Needle Punched Non-Woven Geotextiles
Needle-punched non-wovens are a major type of non-woven geotextile produced by mechanically orienting and entangling fibers. Hundreds of fine needles repeatedly penetrate a fibre web to tangle the fibres into a strong, porous and stable fabric.
Compared to other non-wovens, needle-punched variants have high permeability and drainage capacity along with good puncture resistance. This makes them ideal for filtration and drainage applications.

Types of Needle-Punched Non-Woven Geotextiles
Needle-punched non-wovens can be categorized into three main types based on weight and fiber thickness:
Lightweight Needle Punched Wovens
Made from fine fibres and low fiber weights between 20-100 gsm. Mainly used in applications that do not require high strength.
Medium Weight Needle Punched Non Wovens
Heavier fibers and medium basis weights of 100-250 gsm. Provides moderate strength for functions like separation.
Heavyweight Needle Punched Non-Wovens
Very coarse, thick fibres and high basis weights above 250 gsm. Imparts maximum strength for reinforcement uses.
Selections depend on the target function. Non-woven fabrics can be categorized into lightweight and heavyweight variants.
Key Functions and Applications of Non-Woven Geotextiles
Non-woven geotextiles perform various functions that make them indispensable for major infrastructure and construction projects:
Filtration Applications
The porous structure allows water to pass through while blocking soil particles. This filtration ability is useful in:
- Roadway drainage systems
- Retaining walls
- Landfill drainage
- Water treatment plants

Drainage Applications
Nonwovens have high water flow rates in the principal direction. This makes them excellent for drainage purposes like:
- Landfill drainage layers
- Sports field drainage
- Retaining wall and slope drainage
Separation Applications
The fabric physically separates dissimilar materials. Key applications include:
- Roadway base and subbase separation
- Railroad bed separation
- Foundations separation

Reinforcement Applications
Non-wovens provide reinforcement for additional strength when wrapped around soil. Uses include:
- Embankments over soft soils
- Retaining walls with stacked blocks
- Slopes requiring improved bearing capacity
Erosion Control Applications
The fabric acts as a permeable layer to protect against wind and water erosion while allowing water passage. Some uses are:
- Covering slopes along railways and highways
- Coastal embankments erosion control
- Riverbanks and canal protection
Transportation Applications
Within road construction, non-wovens assist with filtration, separation, drainage and stabilization. Common applications:
- Separation between sub-base and subgrade
- Filtration in edge drains alongside pavements
- Soil stabilization for improved load-bearing
Construction Applications
- Foundations and walls drainage
- Vapor barriers in concrete slabs
- Flooring reinforcement and crack prevention

This demonstrates the versatility of non-woven geotextiles across diverse functions in C&I projects. Their adaptive properties drive widespread adoption.
Key Properties of Non-Woven Geotextiles
Non-woven geotextiles exhibit unique properties derived from their material composition, manufacturing method and overall structure:
Raw Materials
Most non-wovens use polypropylene as the raw material which is cost-effective and provides required properties. High-end variants use polyester or a polypropylene-polyester blend.
Basis Weight
Basis weight is the mass per unit area measured in g/m2. Heavier basis weights produce stronger fabrics with higher puncture resistance. Typical range is from 20 g/m2 to 300 g/m2.
Thickness
Thickness depends on fiber density and varies from 1mm to 15mm. Affects permeability, cushioning ability and separation effectiveness.
Hydraulic Properties
Non-wovens have high water permeability (normal to the plane) and adequate transmissivity. Allows swift drainage while blocking soil passage.
Mechanical Properties
Tensile strength, tear strength, puncture resistance and burst strength are key mechanical properties. Non woven selection depends on the required load capacity.
Endurance Properties
Long-term resistance against environmental exposure, chemicals, microbes and mechanical stresses comes under endurance properties. Requires proper polymer choice.
These characteristics directly impact the effectiveness and lifespan of the non-woven geotextile for its intended function.
Overview of Manufacturing Processes
Non-woven geotextile production involves specialized processes to achieve the desired fiber arrangement and properties:
Web Formation
The first step is creating a uniform web of fibres laid out in overlapping, random orientations using air, mechanical or wet-laid techniques.
Web Bonding
The fiber web undergoes thermal, chemical or mechanical bonding. This interlocks the fibres to impart strength, stability and thickness.
Finishing
Additional treatments enhance properties - for instance, calendering uses heated rollers to achieve smoothness. Fabric edges are trimmed to create rolls.
Testing and Inspection
Extensive testing under certified labs evaluates parameters like strength, permeability, opening size etc. This ensures compliance with specifications.
Keeping manufacturing consistent and monitoring variabilities is vital for non-woven quality assurance. Automation allows scalable production with minimal defects.
Design and Installation Factors for Non-Woven Geotextiles
Proper design, handling and deployment of non-wovens ensures successful project outcomes:

Site Preparation
The installation site must be graded uniformly and cleared of debris/rocks to avoid damage. Burial depth is determined. Subsurface drainage may be added.
Installation Techniques
Non wovens can be unrolled on site and placed loose or tense. Joints are sewn or bonded. Additional layers can be installed to enhance functioning. Fixings like sandbags or pegs may be used.
Seams and Overlaps
Adjoining rolls are overlapped for continuity. End overlaps depend on joint strength. Edges can be sewn, welded, glued or kept loose. Key consideration for soil retention uses.
Design Factors
Careful specifications of geotextile properties like strength, permeability, and opening size based on engineering requirements and testing. Survivability and performance lifetime also key.
Following recommended practices for non-woven deployment optimizes field performance and prevents failures.
Key Benefits and Advantages of Using Non-Woven Geotextiles
Non-woven geotextiles offer numerous benefits that make them advantageous over traditional materials:
Cost-Effectiveness
Made from polypropylene, non-wovens are an affordable alternative to CMP pipe drains or graded aggregates for drainage. Limited overlap joints also reduce the quantity required.
Rapid Drainage Performance
The high porosity provides greater flow capacity compared to sand filters or gravel layers. Useful in applications like retaining walls.
Good Puncture and Burst Resistance
The entangled fibrous structure provides better resistance against punctures during installation compared to woven geotextiles.
Ease of Installation
Flexible, lightweight non-wovens are simpler to install in field conditions compared to rigid materials. No special equipment needed.
Enhanced Properties
Specialized manufacturing processes like calendering and bonding create improved non-wovens with the right balance of filtration, separation, cushioning and strength.
Wider Widths
The ability to produce up to 5m wide rolls compared to just 1m for wovens leads to faster deployment with fewer joints.
These advantages have positioned non-wovens as a material of choice for major construction activities and geotechnical engineering applications.
Applications and Case Studies Demonstrating Non-Woven Geotextiles in Action
Non-woven geotextiles have delivered value across many real-world projects:
Landfill Construction - Needle-punched non-wovens used in leachate collection systems increased design life while reducing clogging through superior filtration compared to gravel layers.
Retaining Wall Drainage - Heat-bonded non-wovens used as wall wraps maintained water drainage and prevented soil washout, keeping 100km of critical rail walls safely stabilized through extreme weather.
Riverbank Protection - Durable non-woven wraps applied on embankments prevented erosion along highly flood-prone rivers through monsoons. Filtered runoff while retaining soil stability.
Roadway Improvement - Calendered non-wovens beneath motorway overpasses provided vital reinforcement to stabilize compressible soil while facilitating drainage and preventing pumping.
Coastal Reinforcement - Wide-width non-wovens encasing sandy coastal cliffs added shear strength and tensile reinforcement. Protected against collapse from rising sea levels and storm surges.
This demonstrates how non-wovens of different compositions can be adapted for specialized needs in infrastructure projects where performance and longevity are critical.
Industry Trends and Ongoing Innovations in Non-Woven Geotextiles
Several interesting trends, developments and innovations are shaping the non-woven geotextiles sector:
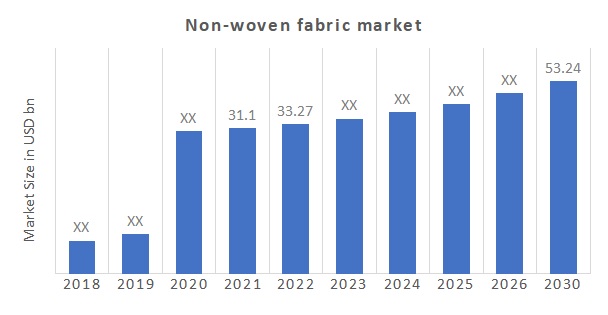
High Growth Potential - The non-wovens market is projected to grow steadily at 6% CAGR driven by major public infrastructure investments and demand from emerging economies.
Raw Material Advances - Enhanced polymers like high-density polypropylene and high-modulus polyester are creating improved non-wovens with greater functionality.
Manufacturing Improvements - Process enhancements and new techniques are allowing more fine-tuned manipulation of fiber properties during production.
Multifunctional Products - Combining non-wovens with drainage nets or reinforcing grids creates single products that provide filtration, separation and reinforcement together.
Application R&D - Ongoing research into novel uses for non-wovens like landfill caps, nuclear waste containment and offshore geotextiles to drive adoption across new domains.
Conclusion
Non-woven geotextiles have become an indispensable resource for civil engineering and infrastructure applications where their high permeability, strength, and versatility can enhance project outcomes and lifespan.
As materials and manufacturing continue evolving, non-wovens are poised to meet more specialized demands. With a thorough understanding of their capabilities, civil engineers can apply these adaptable fabrics for a sustainable future.